Top 10 Common Health Issues Women Face and How to Prevent Them
Reviewed by: Obstetrics and Gynaecology Department
Sarah, a 35-year-old female, has been getting more and more tired these past months. Despite attributing it as just the normal stress from balancing work, family, and personal life, when she realized she's gaining weight unexpectedly, having mood swings, and having her periods irregularly, she finally went to see her doctor. A few tests later, she's diagnosed with thyroid dysfunction. This diagnosis serves not only as a wake-up call for Sarah but also as a reminder to how many women neglect or overlook their own health until it is impossible to do otherwise.
Sarah's story is not unique. Women tend to prioritize their own health last, swept up in the chaos of life. Yet knowing the most prevalent health issues within women and catching the signs before they become more serious can be a lifesaver in avoiding or controlling these conditions.
In India, thyroid disorders are widespread, affecting approximately 11% of adults, with a significantly higher prevalence among women. In some regions, the prevalence among women is as high as 19.6%.
This serves as a crucial reminder for women to prioritize regular health check-ups and be aware of early symptoms that could indicate underlying thyroid issues.
Here, in this blog, we will discuss some of the most common women's health issues, dissect why they happen, and provide actionable advice on how you can avoid them. Empowering yourself begins with knowledge, and that's what we are here for.
Heart disease is a common health problem in women of death worldwide. While many associate heart disease with men, the risk for women is equally significant, especially after menopause. The reasons include hormonal changes, high blood pressure, and an increase in cholesterol levels.
Prevention:
- Maintain a healthy diet low in saturated fats and high in fruits and vegetables.
- Regular physical activity, such as walking or aerobic exercises.
- Regular check-ups for cholesterol, blood pressure, and diabetes management.
Breast cancer is one of the most common women's health issues globally, with a significant number of women diagnosed each year. Early detection through mammograms can make a huge difference in survival rates.
Prevention:
- Regular self-exams and professional screening starting at age 40.
- Healthy lifestyle choices, including maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding alcohol.
- Genetic testing for those with a family history of breast cancer.
Osteoporosis is a condition that causes bones to become weak and brittle, leading to fractures. It is particularly common in older women, especially after menopause, due to a decrease in estrogen levels.
Prevention:
- Ensure adequate calcium and vitamin D intake.
- Engage in weight-bearing exercises, such as walking or strength training.
- Consider medications to help strengthen bones, especially if at higher risk.
Diabetes, particularly type 2, is increasingly prevalent among women. The condition can lead to serious complications, including heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
Prevention:
- Regular blood sugar monitoring and screening, especially if you are overweight or have a family history.
- A balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Regular physical activity, such as 30 minutes of moderate exercise five times a week.


Women are more likely than men to experience mental health issues like depression and anxiety. Hormonal changes related to menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause can contribute to these mental health concerns.
Prevention:
- Regular exercise to boost mood and reduce anxiety.
- Seeking professional help and considering therapy or counseling.
- Practising mindfulness and stress-reduction techniques such as yoga or meditation.
UTIs are one of the most common health problems in women, with women being more prone to them due to the shorter length of their urethra. These infections can be painful and, if untreated, can lead to kidney damage.
Prevention:
- Drink plenty of water to flush out bacteria.
- Urinate after sexual activity to prevent bacteria from entering the urinary tract.
- Wipe from front to back to reduce the risk of infection.
Cervical cancer is a significant concern for women, often caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). Regular pap smears and HPV tests are critical for early detection and prevention.
Prevention:
- Get vaccinated against HPV.
- Regular pap smears and pelvic exams starting at age 21.
- Safe sex practices to reduce the risk of HPV transmission.
Endometriosis is a painful condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus. This often causes infertility, pelvic pain, and heavy periods.
Prevention:
- While there is no definitive way to prevent endometriosis, early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and improve fertility outcomes.
- Pain management strategies, such as anti-inflammatory medications or hormonal treatments.
Menstrual irregularities are common among women of reproductive age, ranging from heavy bleeding to painful periods (dysmenorrhea) and skipped periods. These disorders can interfere with daily life and sometimes indicate underlying health conditions.
Prevention:
- Maintain a healthy diet and manage stress levels.
- Regular physical activity can help regulate periods.
- Seek medical advice if periods become irregular or cause significant discomfort.
Thyroid issues, including hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, are common among women, especially those over 60. These conditions can lead to weight changes, fatigue, and other complications.
Prevention:
- Regular screening for thyroid function, particularly for women over 40 or those with a family history of thyroid disease.
- Maintaining a healthy diet and managing stress can also help regulate thyroid function.
To catch these common health issues for women early, regular screenings are essential. Here’s a quick guide:
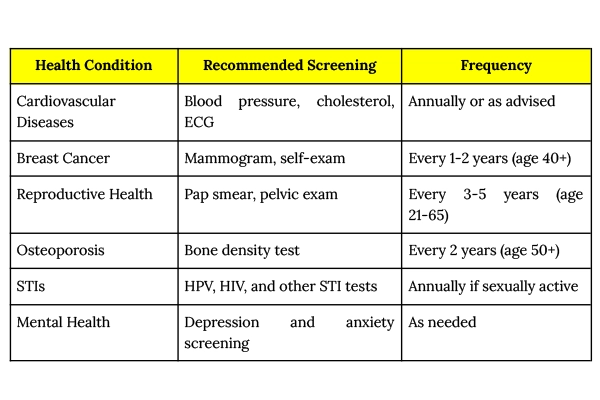
At Manipal Hospitals Global, we understand that women's health requires specialised attention at every stage of life. From preventive care like mammograms and osteoporosis screening to advanced gynaecological treatments, our expert team is dedicated to providing personalised care.
Whether you're managing heart health, mental well-being, or reproductive health, we are here to support you with comprehensive medical services. Prioritise your health today – schedule a consultation with our skilled gynaecologists and take the first step towards a healthier, more fulfilling life. Trust Manipal Hospitals Global for world-class women's healthcare, wherever you are.
For more information on women's health, you can explore these reliable resources:








